Contact us directly to discuss your specific requirements, help you with purchasing, or with any other questions.
This "how-to-connect" documentation will explain the initial configuration of an example connection from an SQL Server to a Office365 / On-Premise SharePoint Library.
This guide presupposes that you have installed the Layer2 Cloud Connector and that you are familiar with its basic functionality. The Layer2 Cloud Connector User Documentation will provide you with all necessary information.
2. Configuring the Layer2 Cloud Connector
2.2 Configuring the Data Entity 1
2.3 Configuring the Data Entity 2
3.2 Limit of files per Blob fields
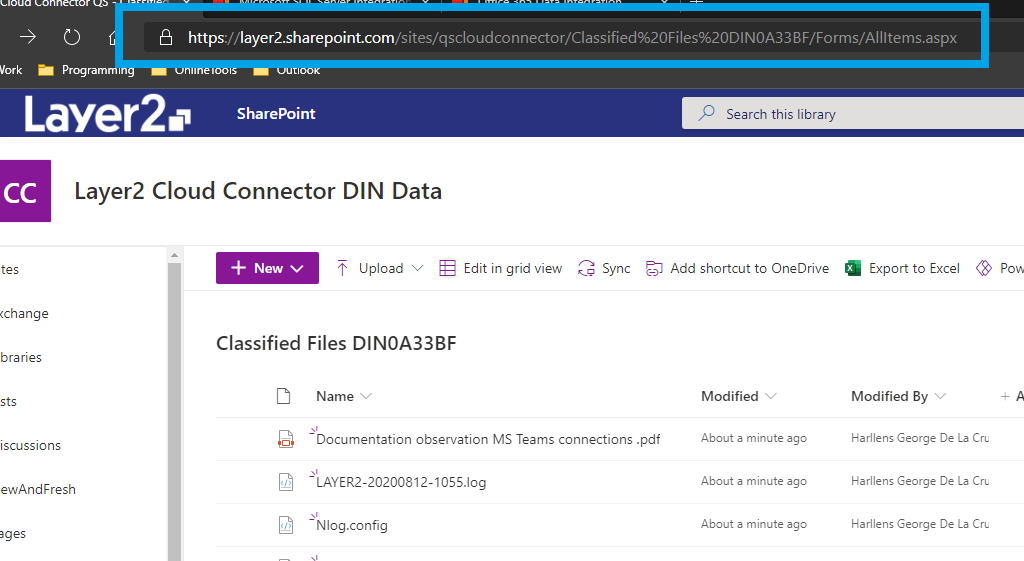
In order to get our SharePoint files we will need to retrieve the SharePoint Online library URL.
Please copy the SharePoint library URL from your internet browser as shown below, as we will need it later for the connection string.
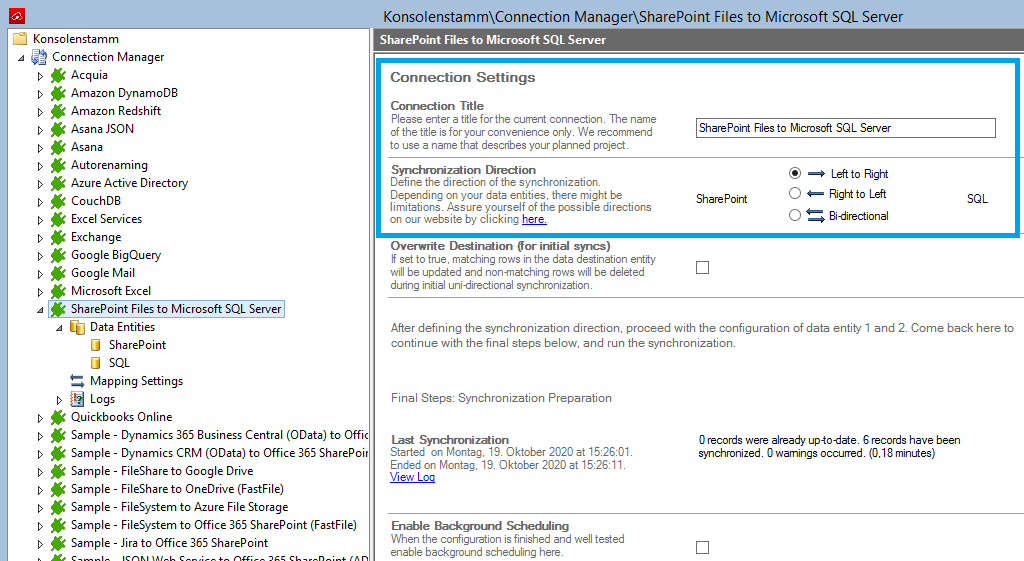
Create a new connection by using the Create New Connection option in the Actions pane (right-hand side). The new connection will appear at the bottom of the Connection Manager List (left-hand side). Click on your newly created connection to open the connection configuration settings.
Choose a meaningful name for your connection and replace the current "New Connection" Connection Title with it.
Although connections to can be bi-directional, an initial connection should always be uni-directional to assure that both data entities are identical before switching to bi-directional. Therefore, choose Left to Right as Direction. You can change this setting after your initial synchronization finished successfully.
We will now set up our Data Entities. Go to the data entity “Data Entity 1” to open the configuration settings.
Choose a Data Entity Title. It is recommended to give your entities meaningful names to maintain a good overview over the two entities.
Select the Data Provider for SharePoint(Layer2) from the data provider list.
You can search for SharePoint by typing into the selection box.
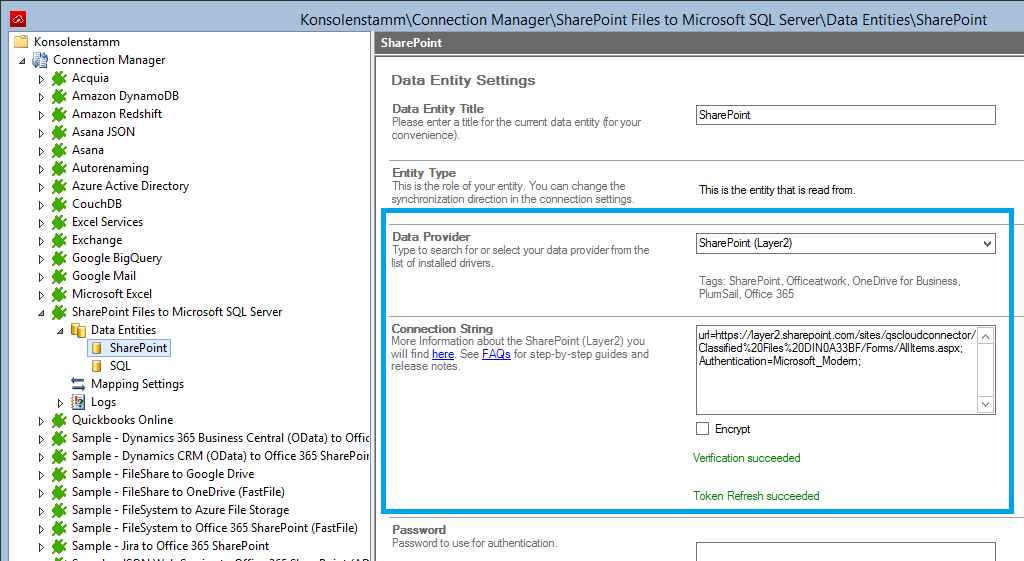
For the Connection String, we need the in step 1 mentioned information. You can copy the below connection string and adjust it to match your gathered information. Use the Verify Connection String option to evaluate if the provided connection string is valid.
URL=https://your_custom_sharepoint_list_url/AllItems.aspx;Authentication=Microsoft_Modern
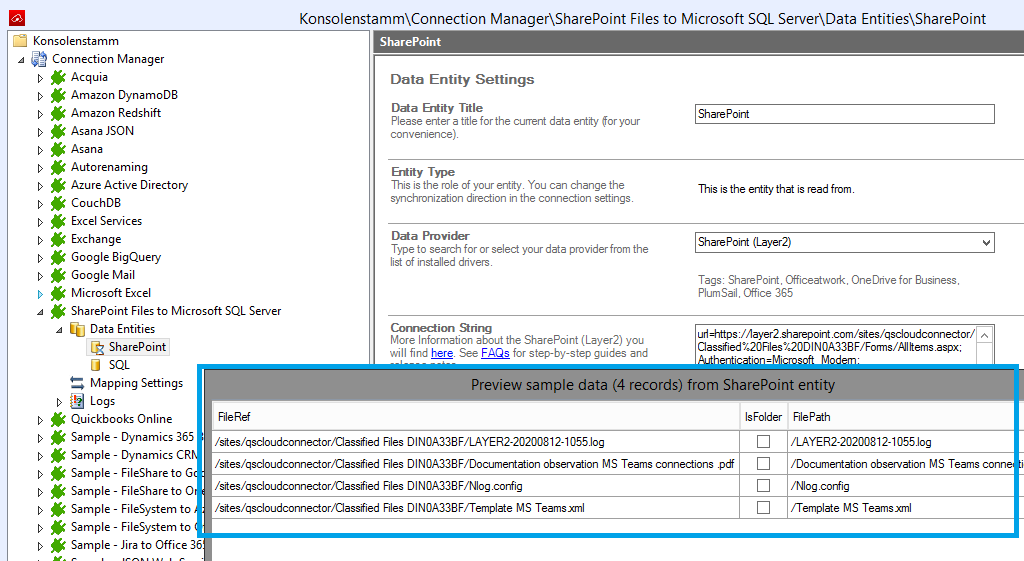
To check your data before synchronizing you can use the Preview Data option on the right-hand pane, it will provide you a pop-up window showing the data to be synced from your SharePoint library as shown below.
We are going to send the data to your Microsoft SQL Server table. It's required that you set up the SQL table prior to the next steps. Your table should contain matching columns according to your source entity.
Use the left-hand pane to switch to the data entity "Data Entity 2". We will be using the Data Provider for SQL Server for this setup.
You can copy the below Connection String which contains the minimum of required properties to connect to your SQL server table.
Data Source=myServer; Initial Catalog=myDatabase; User Id=mySQL_User;
Enter the password that belongs to the user account used in the connection string into the Password field. Save your changes by using the right-hand pane option Save Changes.
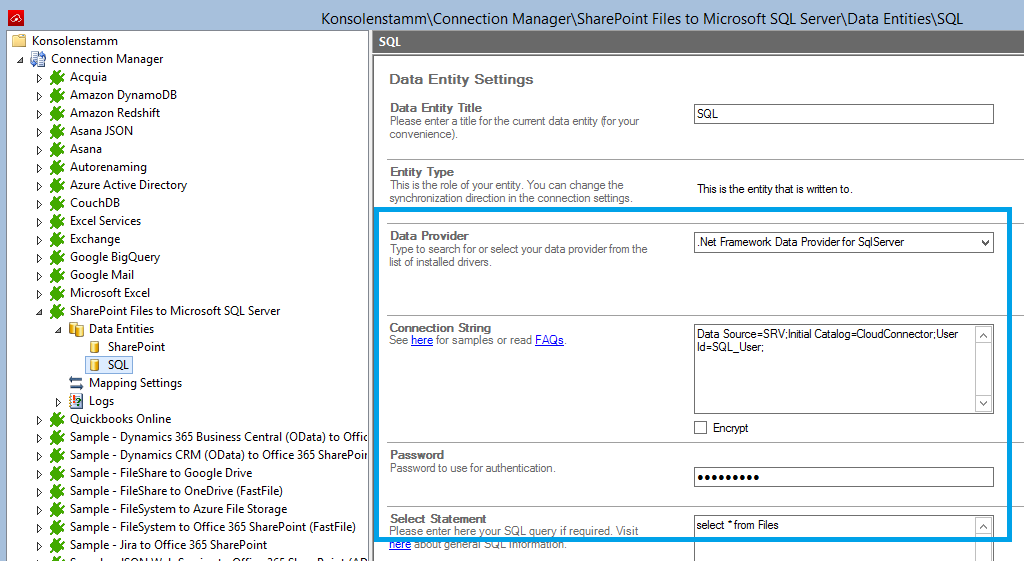
In the next step, we will configure our mapping settings. Click on the Mappings option on the left-hand pane. If your fields from SharePoint are named identical to the fields from your SQL table, the Enable Auto Mapping option will match those columns. Disabling this option allows you to match your columns as needed manually. We enabled auto-mapping in our setup. Save your changes by using the right-hand pane option Save Changes.
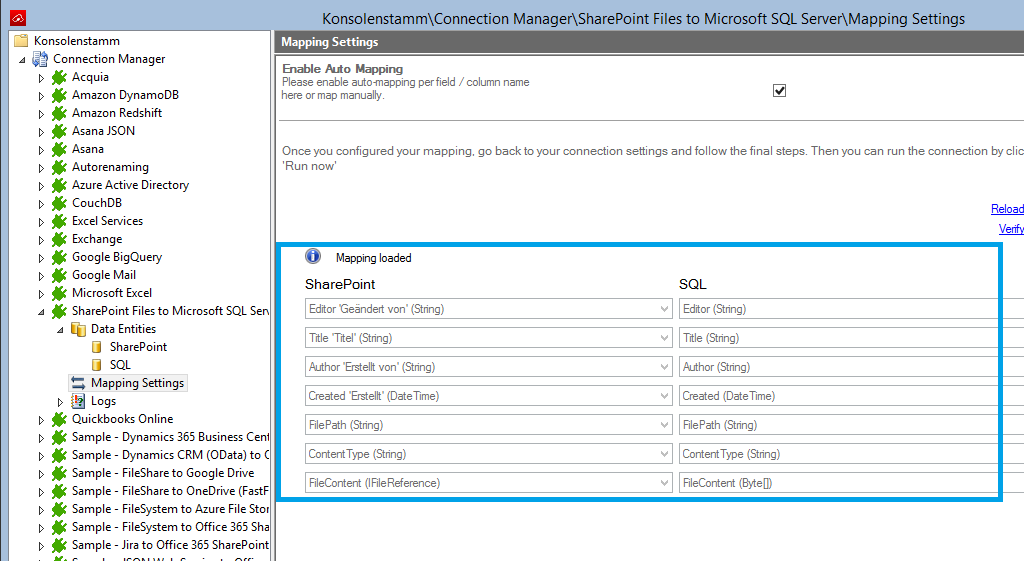
To run your connection switch back to the main connection configuration node and use the Run Now Button located on the bottom of the setup page. The Run Synchronization Toolbox will also display the synchronization process.
Below is a data preview of the information we have accessed in our source entity:
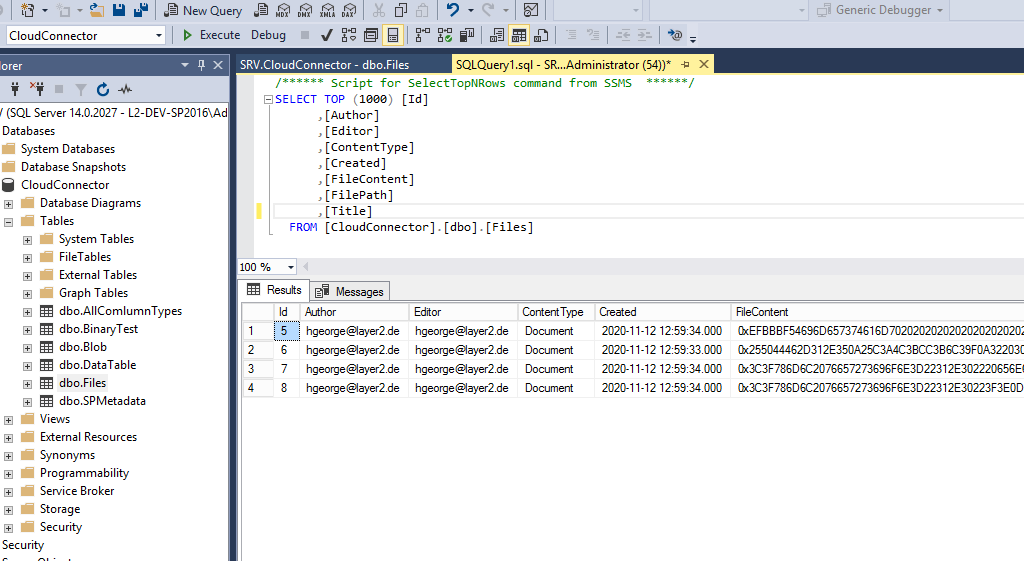
This will be the result in our SQL Table after our initial successful synchronization:
If you want to use a bi-directional synchronization, you can now switch your connection direction after our first initial synchronization run finished successfully. After adjusting the direction, you should check your Mappings settings again because some systems might include read-only columns that cannot be mapped directly.
We also recommend to choose a Conflict Resolution that matches your environments needs. You can find out more about the different conflict resolutions in our Layer2 Cloud Connector User Documentation.
Complex SharePoint fields like lookups, user or group picker etc. are generally supported. You have to make sure providing values that fit into the fields. If not possible, you can workaround by synchronizing text fields only and add your business logic using triggers and stored procedures (in SQL) or workflows (in SharePoint).
This connection supports uni-directional as well as bi-directional synchronizations. Your query must be updatable for this (note that most joins are not). You also need to have write access rights to SQL for two-way synchronizations.
Please keep in mind that each BLOB field can handle up to 2 GB of data (except for Unicode type where its 1 GB) in MS SQL Server.